POLYHOUSE CULTIVATION is farming under full controlled condition, temperature, humidity, water fertilizers everything is automated. If done rightly around 6-7 lakhs net profit can earned in a year on one acre. Generally Cucumber, Summer squash, Broccoli, Brinjal, Tomato, Bell pepper and horticulture cut flowers can be cultivated in polyhouse. The crops grown in open field are exposed to vivid environmental conditions like attack of insects and pests, whereas the polyhouse provides a more stable environment.
Based on environmental control system, polyhouses can be divided in to two types
a) Naturally ventilated polyhouse
These polyhouse do not have any environmental control system except for the provision of adequate ventilation and fogger system to prevent basically the damage from weather aberrations and other natural agents.
b) Environmental controlled polyhouse
This type of polyhouse helps to extend the growing season or permits off-season production by way of controlling light, temperature, humidity, carbon-dioxide level and nature of root medium.
Based on the suitability and cost, polyhouses can be divided into
a) Low cost or low tech polyhouse
Low cost polyhouse is a simple structure constructed with locally available materials such as bamboo, timber etc. The ultra violet (UV) film is used as cladding materials. Unlike conventional or hi-tech polyhouses, no specific control device for regulating environmental parameters is provided. Simple techniques are, however, adopted for increasing or decreasing the temperature and humidity. Even light intensity can be reduced by incorporating shading materials like nets. The temperature can be reduced during summer by opening the side walls. Such structure is used as rain shelter for crop cultivation. Otherwise, inside temperature is increased when all sidewalls are covered with plastic film. This type of polyhouse is mainly suitable for cold climatic zone.
b) Medium-tech polyhouse
Polyhouse users prefers to have manually or semiautomatic control arrangement owing to minimum investment. This type of polyhouse is constructed using galvanized iron (G.I) pipes. The canopy cover is attached with structure with the help of screws. Whole structure is firmly fixed with the ground to withstand the disturbance against wind. Exhaust fans with thermostat are provided to control the temperature. Evaporative cooling pads and misting arrangements are also made to maintain a favorable humidity inside the polyhouse. As these systems are semi-automatic, hence, require a lot of attention and care, and it is very difficult and cumbersome to maintain uniform environment throughout the cropping period. These polyhouses are suitable for dry and composite climatic zones.
c) Hi-tech polyhouse
To overcome some of the difficulties in medium-tech polyhouse, a hi-tech polyhouse where the entire device, controlling the environment parameters, are supported to function automatically.
Cost involved for the construction:
1 Less expensive polyhouse without fan - Rs.300 to 500/m2
2 Medium cost polyhouse with pad and fan system (without automation) - Rs.800 to Rs.1100/m2
3 Expensive polyhouses with fully automatic (control system) - Rs.2000 to Rs.3500/m2
Polyhouse cultivation is used mainly for the following purposes
- Raising of seedlings in the nursery
- Raising of exotic vegetables like broccoli, lettuce, water melon, summer squash etc
- Raising of vegetable crops like Capsicum, Tomato, Cucumber, Brinjal, Cabbage
- Growing plants in polyhouses for hybrid seed production of flowers
- Growing plants for cut flower production.
- Growing potted ornamental plants.
COST ESTIMATION FOR POLYHOUSE CONSTRUCTION
Title of the project: Production of Rose cut flowers for domestic and export market.
The major project components required for cut flower production in polyhouse are as follows
- Land procurement
- Polyhouse construction (including the materials)
- Planting material
- Irrigation
- Fertilization system
- Grading and packing room
- Refrigerated van
- Office equipment
- Import of technology
- Labor charges
- Technical manpower
- Pesticides, Fertilizers, preservatives
Classification of major cost components
A. Fixed cost –Permanent items
B. Recurring cost –planting, cultivation, maintenance, storage, packing and transportation costs.
Budget requirement to produce Rose cut flowers in one hectare polyhouse area
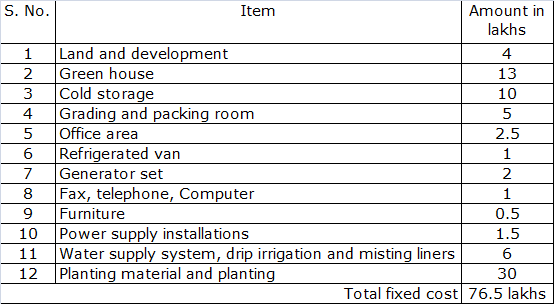
A. Fixed cost
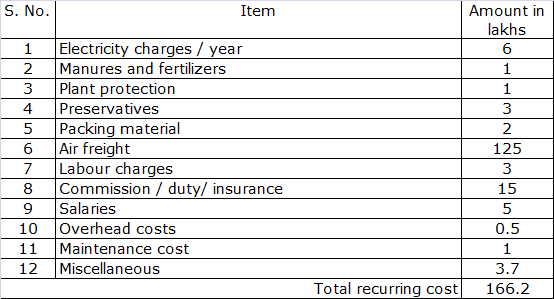
B. Recurring costs
Total investment for the project = Fixed cost + Recurring cost = 76.5 + 166.2 in first year= 242.7 lakhs
Project yield
No. of rose plants per hectare of polyhouse = 60,000
No. of flowers expected per plant = 100 to 150
No. of exportable quality flowers /plant = 60 to 100
Price per flower in international market = Rs. 6 to 11
Total exportable flowers /ha @ 100 flowers /plant = 60 lakhs flowers
Gross income through exports @ 50 flowers/plant = 300 lakhs (minimum).
Major advantages of polyhouse cultivation
• Increase in production capacity by reducing crop time.
• High quality of the polyhouse product
• Uniformity in plant growth with good vigour
• Provide quick take off with little or no transplanting shock.
• Easy maintenance of sanitation measures
• Easy to handle, grade and shift for transportation.
• Better water drainage and aeration in pot media.
• Easy to monitor chemical characteristics and plant nutrition with advanced irrigation systems like drips.
CONCLUSION:
The yield under polyhouse cultivation can be achieved to the level of 4 to 8 times as compared to the open field crop cultivation. Various research trials conducted at agro research centers in Northern India indicated that Tomato (Northern planting), Capsicum (Planted in mid September) and Cucumber (Planting in mid October) under polyhouse produced 1550 Kg, 1500 Kg and 1100 Kg per 100 square meter. The duration of these vegetable crops were 4-10 months and more than 90% of total yield is achieved during the off season which fetches higher market price (2-4 times than normal season price). Further the crop duration can be extended up to July or August with the application of micro irrigation and fertilizers and yield can be achieved to the level of 20-25 Kg/square meter. Therefore it is possible to harvest single crop throughout the year with the minimum additional application of inputs and higher returns can be achieved.