 Major soluble constituents of irrigation water are -
Major soluble constituents of irrigation water are -
Cations +
Ca2+
Mg2+
Na+
K+
Anions -
SO4 2-
HCO3 -
CO3 2-
Cl-
Other elements viz.,
Li,Si,Cu,I,Ni,Co,F,B,Ba,Ar,
Sb,Bi,Cr,Mn,Pb,Mo,Se,PO4 and organic materials.
 Factors affecting soluble salts in ground water
Factors affecting soluble salts in ground water
Physico chemical char. of the parent rock
Climate of the area
Micro organism present in the area.
Mineralogical characteristics of the soil
Topography
Sea water intrusion in coastal areas.
Human interference.
Irrigation Water Quality Criteria
Salinity hazard – Total soluble salt
Specific ion toxicity hazard
Sodicity hazard – Relative proportion of Na
Alkalinity hazard – Relative Bicarbonate
concentration
 Solubility of salts in water
Solubility of salts in water
Salts of high solubility
CaCl2
MgCl2
NaCl
MgSO4
NaHCO3
Na2SO4
Salinity hazard
Salt Concentration 80 me/l at field capacity
Salt Concentration 40 - 50 me/l at saturation
Salinity hazard
Salt Concentration 80 me/l at field capacity
Salt Concentration 40 - 50 me/l at saturation

EC and Salinity
EC VALUE dS/M SALINITY HAZARD
0.25 VERY LOW
0.25- 0.75 LOW
0.75 -2.25 MEDIUM
2.25-5.0 HIGH
5.0 VERY HIGH
0.25 EXCELLENT FOR ALL SOIL
0.25-0.75 NOT SUITABLE FOR HEAVY SOILS AND SENSITIVE CROPS
0.75 - 1.50 SOIL WITH MODERATE TO GOOD PERMEABILITY
1.50 - 3.0 PERMEABLE SOIL WITH TOLERANT CROPS
3.0 USE ONLY AS SUPPLEMENTARY SOURCE
0.25 LOW SALINITY
0.25- 0.75 MEDIUM SALINITY
0.75- 2.25 HIGH SALINITY
2.25 - 5.0 VERY HIGH SALINITY
 STANDARDS OF GROUND WATER WITH RESPECT TO SOILS
STANDARDS OF GROUND WATER WITH RESPECT TO SOILS
NATURE OF SOIL EC dS/m for crops
semi tolerant tolerant
deep black soil and alluvial soil 1.5 2.0
30 % clay ( fair to moderate drainage)
Heavy textured soil , clay 20-30 % , good drainage 2.0 4.0
Medium textured soil ,clay 10-20 % , good drainage 4.0 6.0
light textured soil , clay <10% excellent drainage 6.0 8.0
PH AND SALINITY
TOTAL SOLUBLE SALTS IN ppm SUITABLE PH UNSUITABLE PH
<400 <9 >9
400-600 < 8.5 >8.5
600-800 <8 >8
800-10000 doubtful for irrigation
10000 unsuitable for irrigation
chloride and salinity
2 me/litre is safe for cultivation
 Chloride and Sulphate salinity
Chloride and Sulphate salinity
CHLORIDE dS/m SULPHATE dS/m CROP GROWTH
4 6 100 % growth
4-8 6-12 80-90 % growth
8-12 12-20 50-70 % growth
12-20 20-40 20-50 % growth
20 <40 0
 Chloride hazard for Citrus
Chloride hazard for Citrus
EC dS/m CHLORIDE me/lit FOR CLEY SOIL
1.2 6 NO RISK
1.2 - 1.5 6 - 7.5 LOW RISK
1.5- 1.75 7.5 - 9 MEDIUM RISK
1.75 - 2.25 9-15 NOT SUITABLE
POTENTIAL SALINITY
GOOD PERMEABLE MEDIUM PERMEABLE LOW PERMEABLE
GOOD <5 <3 <3
SATISFACTORY 5-20 3-15 3-7
NOT SUITABLE >20 >15 >7
 Residual Sodium Carbonate (me/l
Residual Sodium Carbonate (me/l
DEGREE OF PROBLEM LIMITS
NO PROBLEM <1.25
INCREASING PROBLEM 1.25 - 2.5
SEVERE PROBLEM >2.5
 Residual Sodium Bicarbonate (me/l
Residual Sodium Bicarbonate (me/l
DEGREE OF PROBLEM LIMITS
NO PROBLEM <10
SEVERE PROBLEM >10
SOLUBLE SODIUM PERCENTAGE
DEGREE OF PROBLEM LIMITS
No problem <60
increasing problem 60- 75
not suitable >75
 Magnesium to Ca + Mg Ratio
Magnesium to Ca + Mg Ratio
DEGREE OF PROBLEM LIMITS
No problem <0.5
Not suitable >0.5
BORON CONTENT IN ppm
DEGREE OF PROBLEM BORON LIMIT
No problem 0.5
increasing problem 0.5 - 2.0
severe problem >2
 Boron Tolerant Crops
Boron Tolerant Crops
TOLERANT CROPS SEMI TOLERANT CROPS SENSITIVE CROPS
Palmyra palm sunflower Apple
dates potato orange
onion tomato grapes
cabbage wheat citrus
 Sodium Adsorption Ratio
Sodium Adsorption Ratio
SAR VALUE WATER QUALITY
0-10 low injury to crops
10-18 can be used with management technologies
18-26 not suited to most crops
26 not suited for irrigation
 Classification of irrigation water quality
Classification of irrigation water quality
PH EC dS/m SAR RSC (m2/L ) NATURE OF WATER
6.5 - 8.0 <0.5 <15 - GOOD
8.0- 8.4 0.5 - 2.0 15-20 <2.5 MEDIUM
8.4 >2 >25 >2.5 UNSUITABLE
 Classification of irrigation water quality
Classification of irrigation water quality
QUALITY OF WATER EC dS/m PH Na% CHLORIDE me/lit SAR
EXCELLENT 0.5 6.5 - 7.5 30 2.5 1
GOOD 0.5-1.5 7.5-8.0 30-60 2.5 - 5.0 1.0-2.0
FAIR 1.5- 3.0 8.0- 8.5 60-75 5.0-7.5 2.0-4.0
POOR 3.0-5.0 8.5 - 9.0 75-80 7.5 - 10 4.0-8.0
VERY POOR 5.0-6.0 9-10 80-90 10-12.5 8.0-15
UNSUITABLE > 6 >10 >90 >12.5 >15
Management aspects
Application of FYM etc., improves permeability and structure.
Keeping gypsum gunny bags in the channel increases calcium content.
Conjunctive use of poor quality water with good quality water.
Incorporating green manure crops.
Application of increased fertilizer dose N-as AmSO4 ,P- as Super PO4 and DAP.
Improve drainage.
Raising salt tolerant crops – cotton, ragi, sugar beet, paddy, ground nut, sorghum, maize, sunflower, chillies, tobacco, onion, tomato, garden beans, amaranthus and lucerne.
Special considerations while using poor quality of water
Saline water having SAR > 20 and
Mg/Ca > 3 leads to water stagnation - Apply gypsum .
Leave the field fallow during rainy season.
Cl/SO4 > 2.0 addition of P.
Use canal water in conjunction with saline water during early crop stage.
Addition of 20% extra seed rate.
 I. MANAGEMENT OF SALINE WATER
I. MANAGEMENT OF SALINE WATER
Tillage – Loosen the dense sub-soil
- percolation of salts & Root penetration
Induction of Salt hardiness
Treating the seeds/Seedling with salt solution
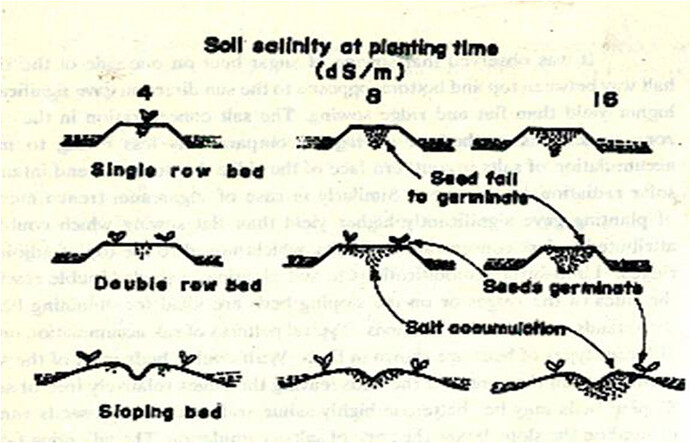
Method of planting broad bed / furrows
Higher seed rate/Aged seedlings
 II. PLANTING TECHNIQUE
II. PLANTING TECHNIQUE
III. IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT
Optimum Irrigation Interval – Less quantity of water and more frequent Irrigation keeps Soil moisture at max. and the salt concentration (OP) will be at a minimum
Drip and Sprinkler system of irrigation
Pre sowing Irrigation
Salts accumulate in the top soil during non crop period
Heavy pre sowing irrigation will leach surface salts and improve germination & early growth

IV. MULCHING
Mulches reduce the water losses by evaporation and reduce salts accumulation
Prevent upward movement of salts to the surface
Appreciable improvement in the water permeability

Growing Salt tolerance of crops

Tolerant
Field crops:
Barley, sugar beet, cotton, sugarcane
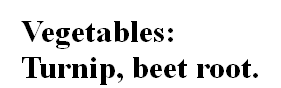
Vegetables:
Turnip, beet root.

Fruits:
Date palm, coconut.
 Semi Tolerant
Semi Tolerant
 Rice, sorghum, maize,
Rice, sorghum, maize,
red gram.
 Tomato, cabbage, cauliflower, potato, carrot, onion.
Tomato, cabbage, cauliflower, potato, carrot, onion.
 Sensitive
Sensitive
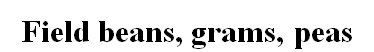 Field beans, grams, peas
Field beans, grams, peas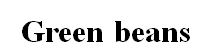 Green beans
Green beans
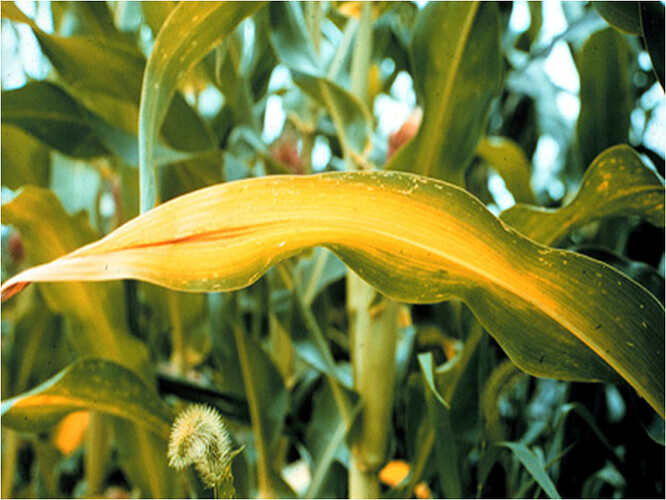
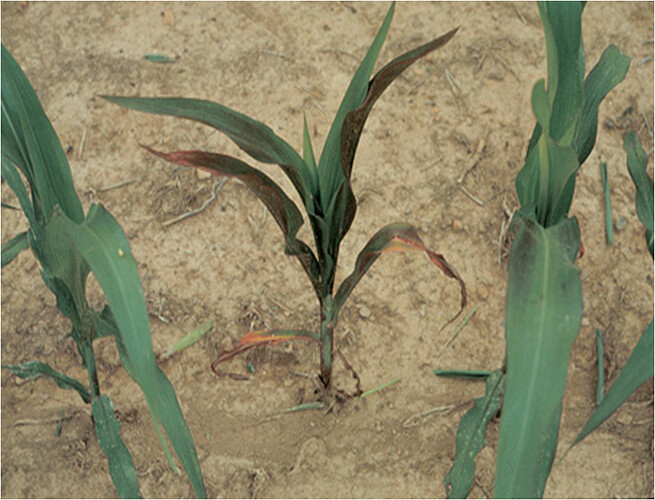
 EFFECT OF SALINITY ON RICE
EFFECT OF SALINITY ON RICE
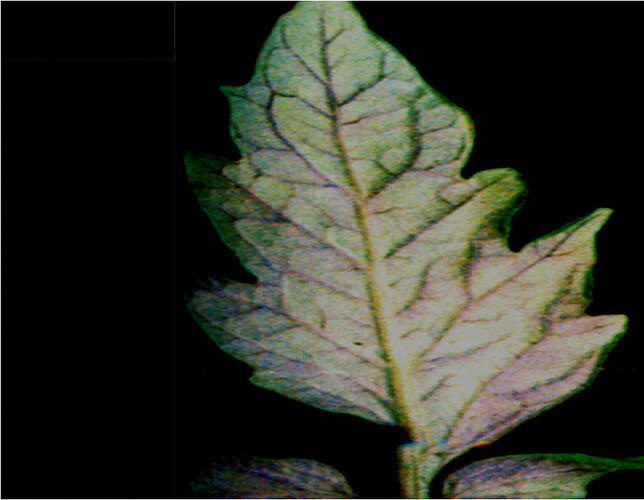
EFFECT OF SALINE SODIC
WATER ON RICE IN HEAVY CLAY SOILS
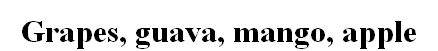
Grapes, guava, mango, apple








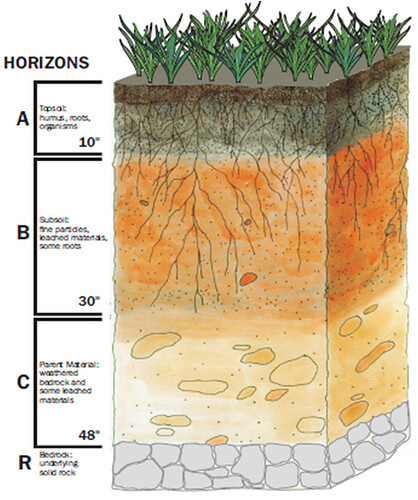
 Brief Description of the Soil Orders
Brief Description of the Soil Orders
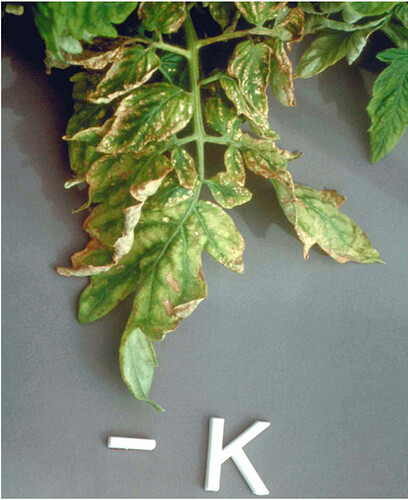
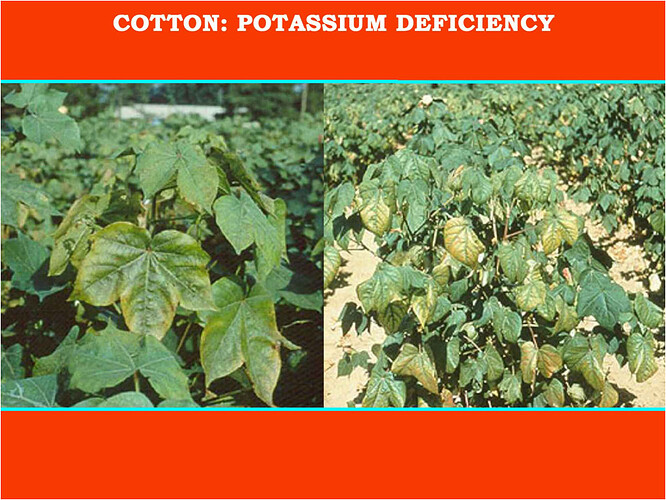
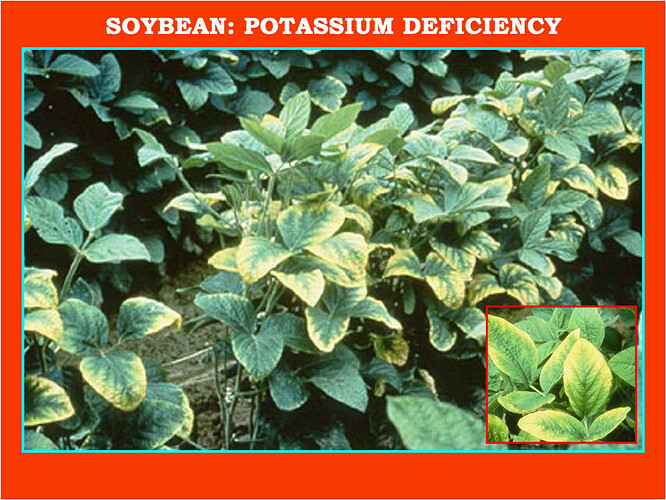
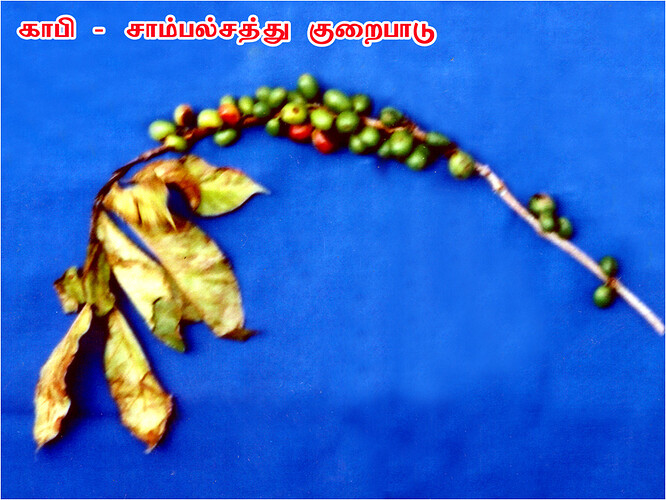
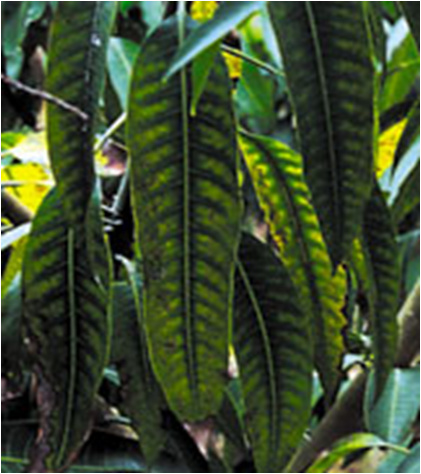
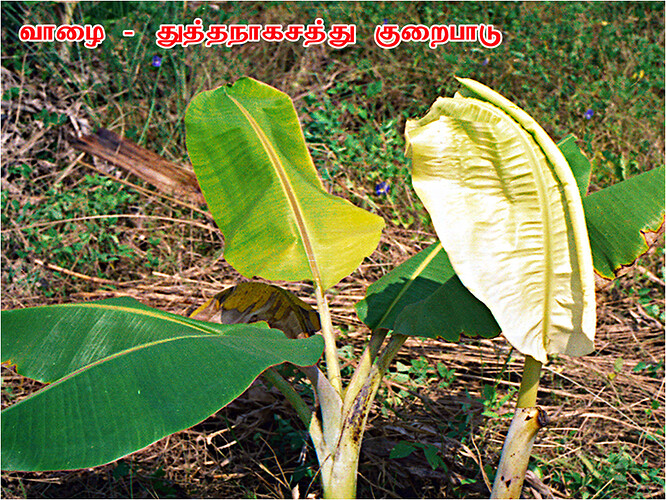
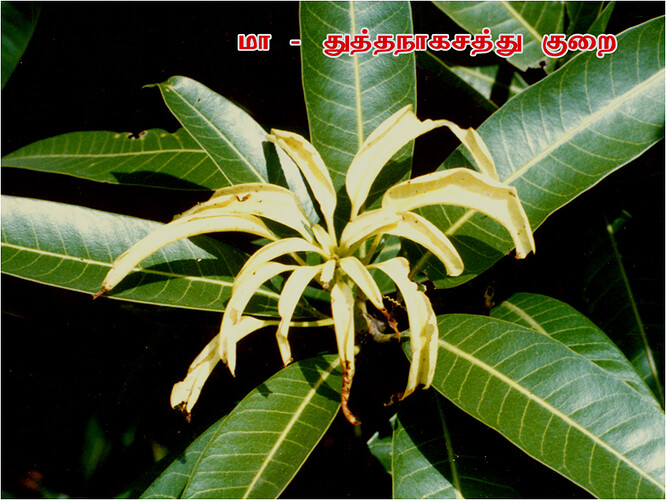
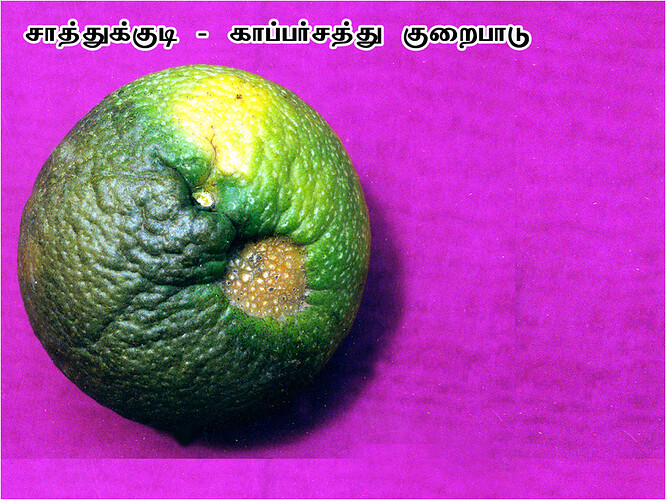
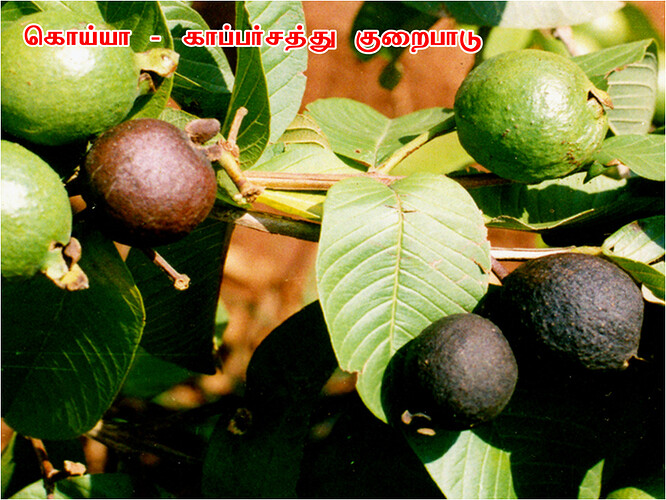
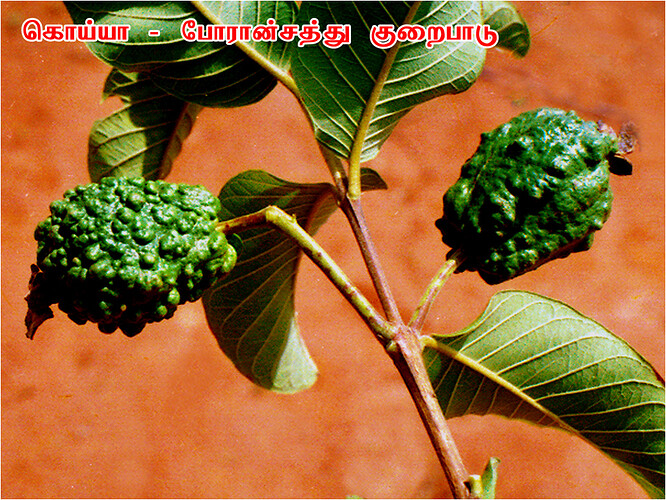
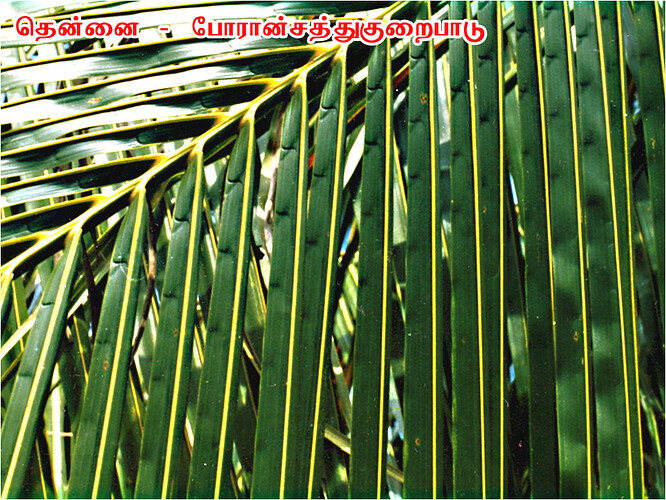
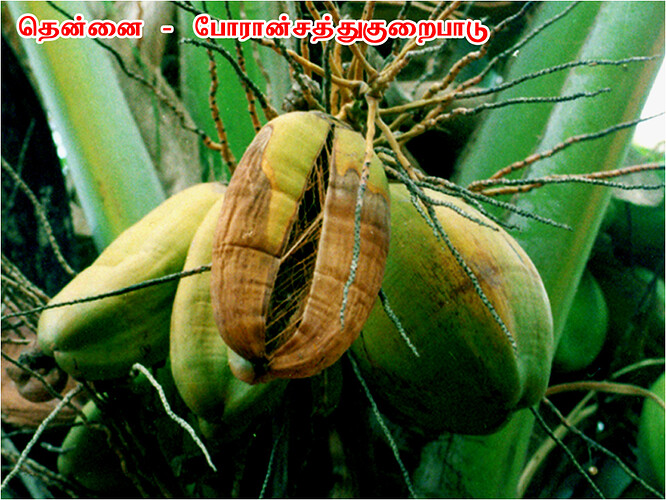
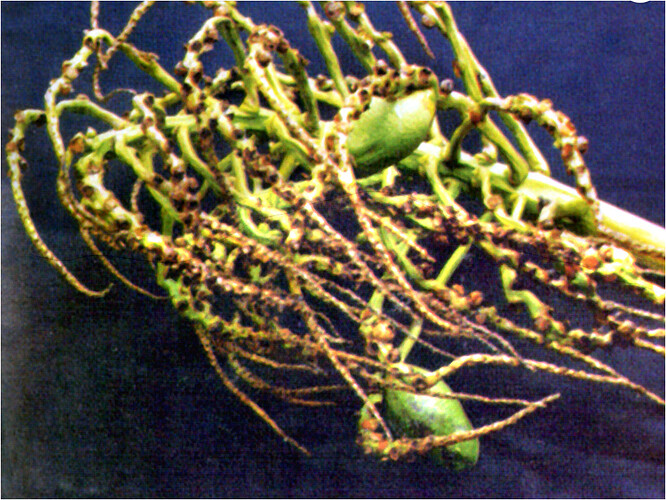
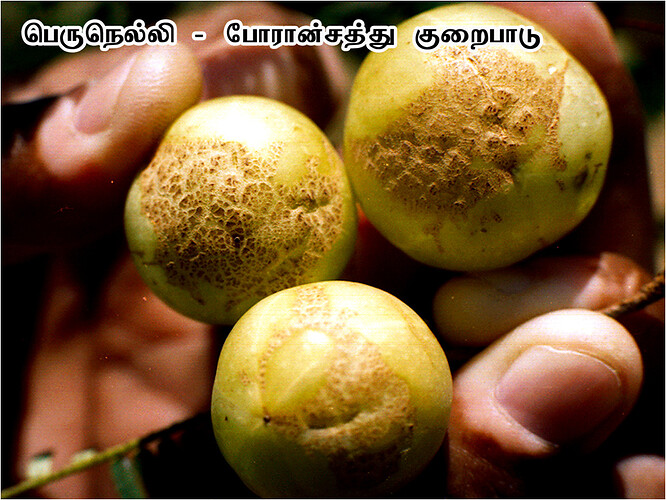
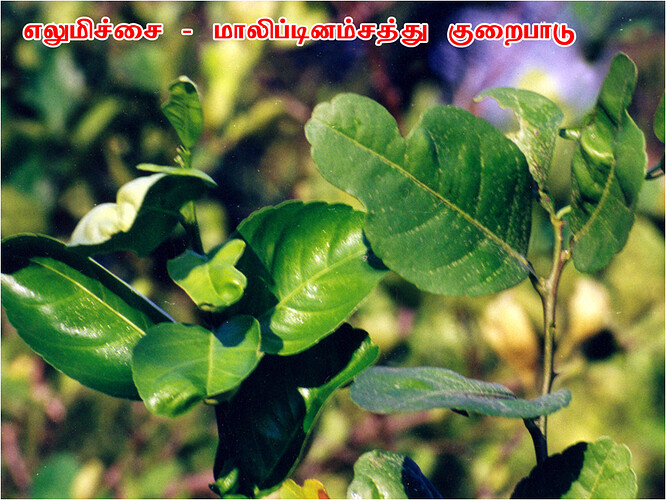
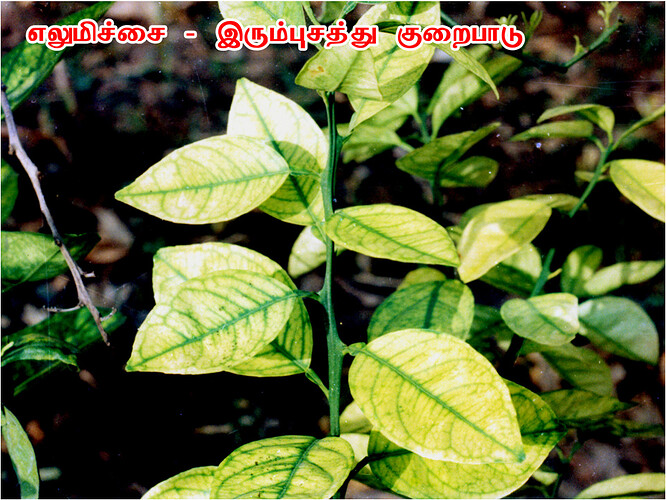
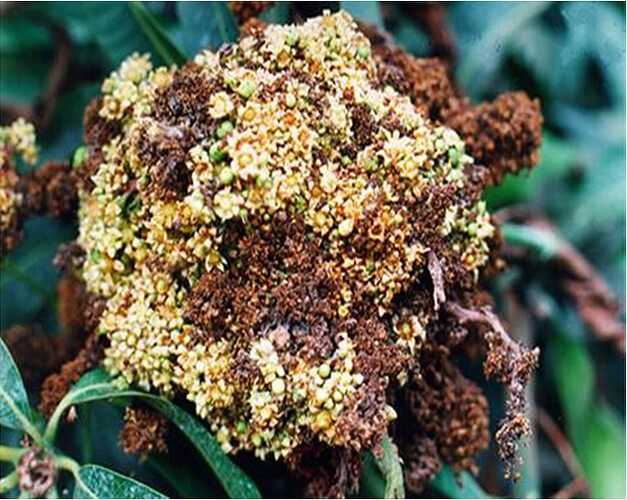
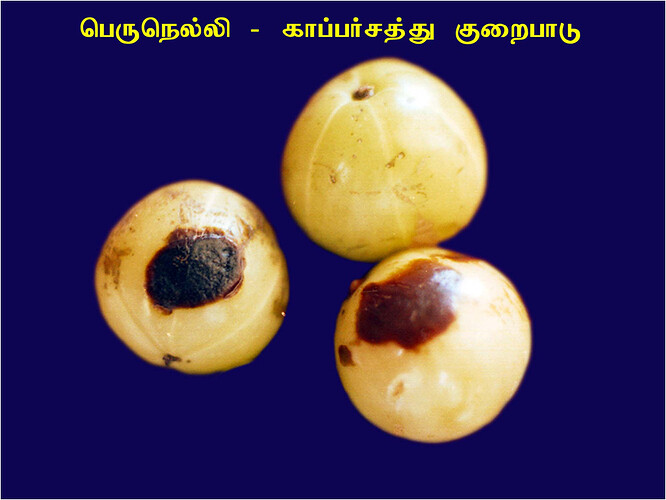
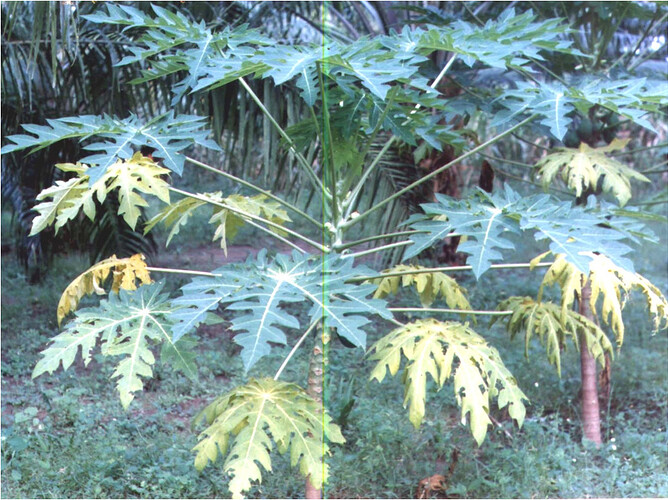
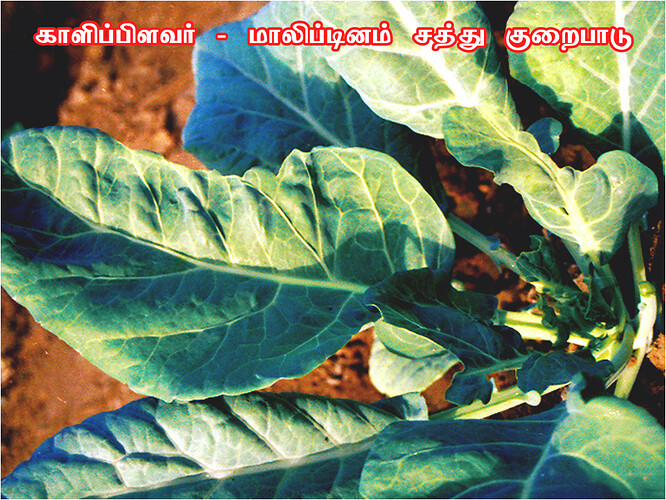











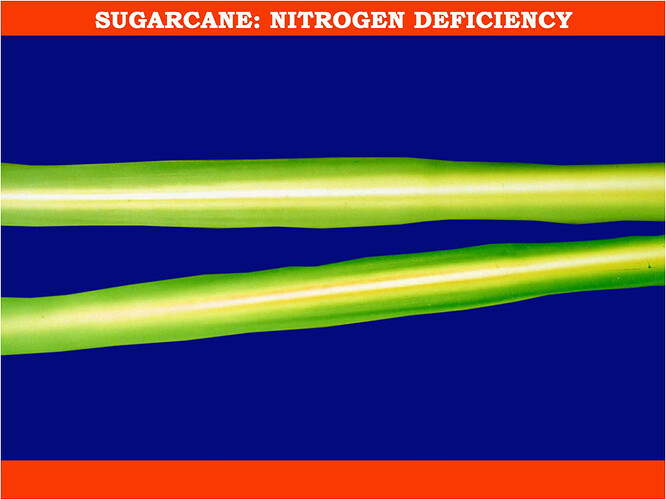






























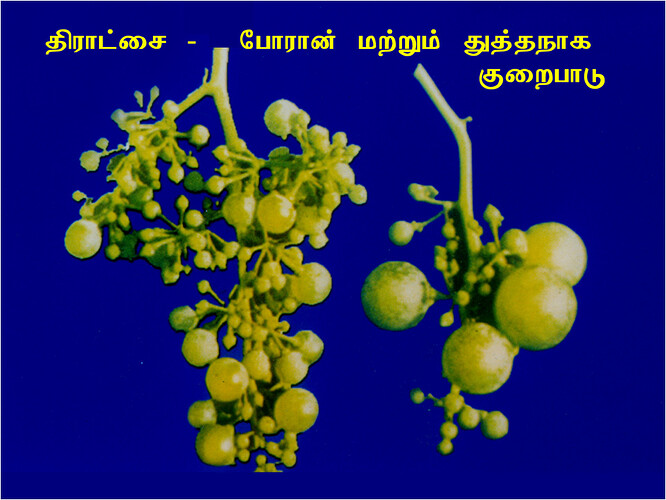









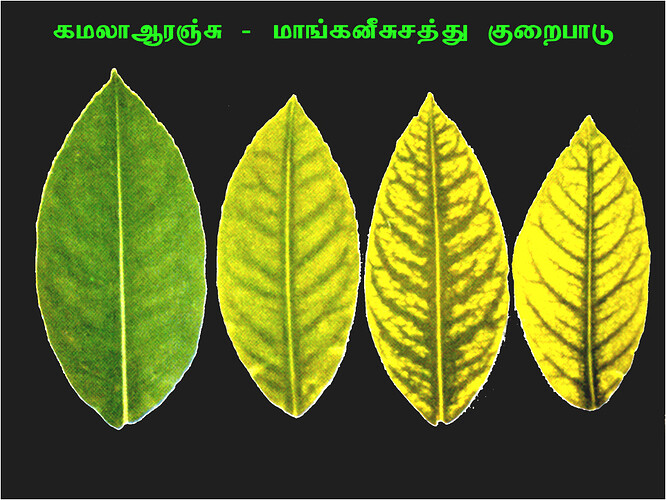












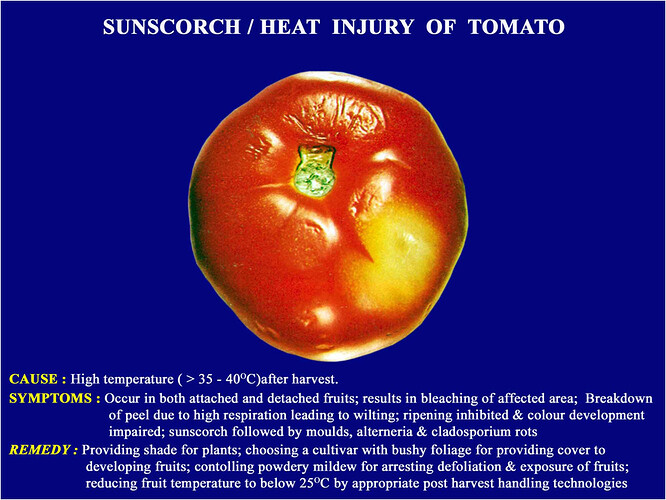

 Major soluble constituents of irrigation water are -
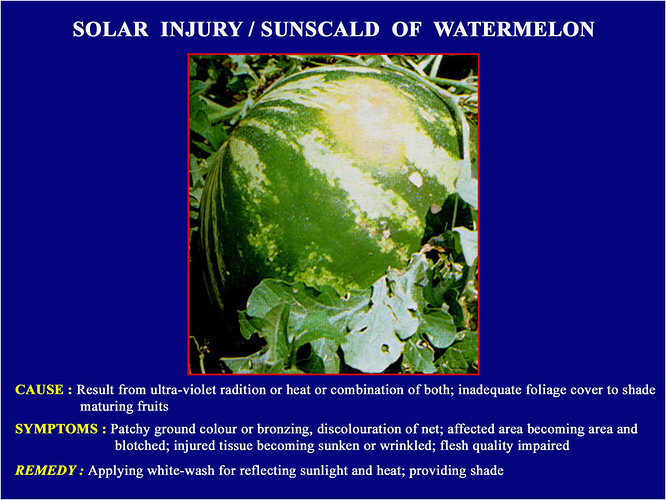
Major soluble constituents of irrigation water are -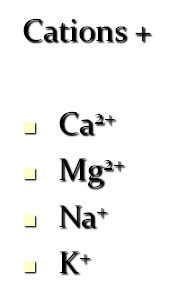
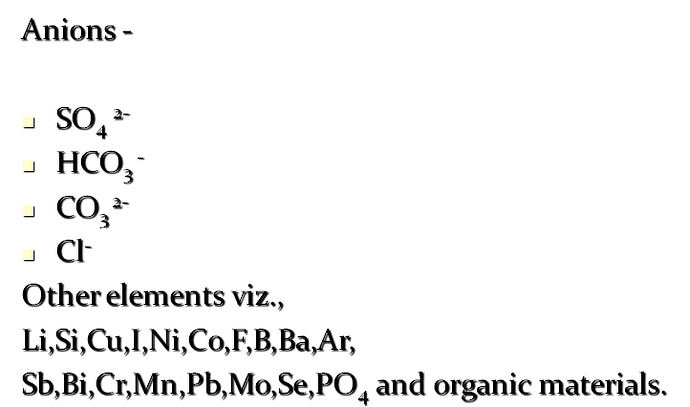
 Factors affecting soluble salts in ground water
Factors affecting soluble salts in ground water
 Irrigation Water Quality Criteria
Irrigation Water Quality Criteria
 Solubility of salts in water
Solubility of salts in water
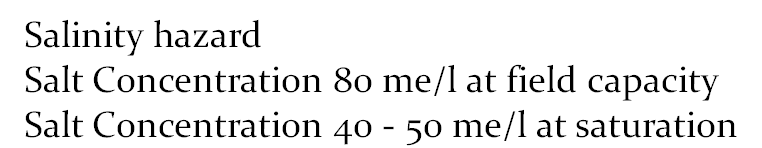
 EC and Salinity
EC and Salinity Chloride and Sulphate salinity
Chloride and Sulphate salinity Chloride hazard for Citrus
Chloride hazard for Citrus Residual Sodium Carbonate (me/l
Residual Sodium Carbonate (me/l Residual Sodium Bicarbonate (me/l
Residual Sodium Bicarbonate (me/l Magnesium to Ca + Mg Ratio
Magnesium to Ca + Mg Ratio Boron Tolerant Crops
Boron Tolerant Crops Sodium Adsorption Ratio
Sodium Adsorption Ratio Classification of irrigation water quality
Classification of irrigation water quality
 I. MANAGEMENT OF SALINE WATER
I. MANAGEMENT OF SALINE WATER
 III. IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT
III. IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT

 IV. MULCHING
IV. MULCHING
 Growing Salt tolerance of crops
Growing Salt tolerance of crops Tolerant
Tolerant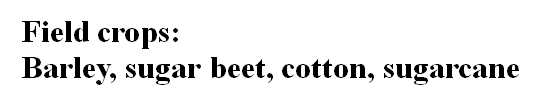 Field crops:
Field crops: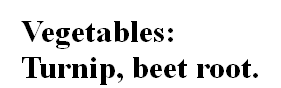 Vegetables:
Vegetables: Fruits:
Fruits: Semi Tolerant
Semi Tolerant Rice, sorghum, maize,
Rice, sorghum, maize, Sensitive
Sensitive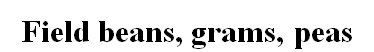 Field beans, grams, peas
Field beans, grams, peas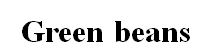 Green beans
Green beans EFFECT OF SALINITY ON RICE
EFFECT OF SALINITY ON RICE









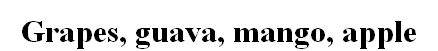 Grapes, guava, mango, apple
Grapes, guava, mango, apple