Soil application
Soil application
Foliar application
Root feeding
Trunk feeding
Fertigation
 Soil application
Soil application


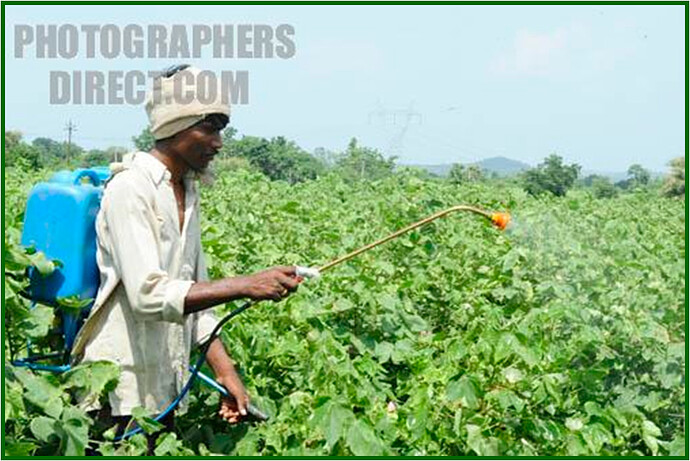
 Foliar application
Foliar application
It is otherwise called as Foliar feeding – Foliar nutrition
A technique of feeding nutrients to plants in the form of liquid directly to their leaves

Use Hand Operated Sprayer for Nutrient Spray

 Advantages of foliar application
Advantages of foliar application Require less quantity of nutrients
Require less quantity of nutrientsLow cost and Quick response - immediate effect
 Uniform application is easily obtained
Uniform application is easily obtainedDeficiencies can be corrected during the growing season
 Low residue
Low residue Highly efficient
Highly efficient
Timely application – need based
Source of nutrient - Concentration - Dose
Time of spray
Good quality water
Type of sprayer
Use of Surfactants is essential
 Foliar Recommendation
Foliar Recommendation
FOLIAR RECOMMENDATION
NUTRIENTS SOURCE CONCENTRATION
NITROGEN Urea <2%
PHOSPHORUS SSP/MAP <2%
POTASIUM MOP/SOP <2%
CALCIUM CaCl2 0.5%
MAGNESIUM MgSo4 0.5%
SULPHUR Any Sulphate FERT 0.5%
IRON FeSo4 0.5%
BORON Borax 0.35
COPPER CuSo4 0.1%
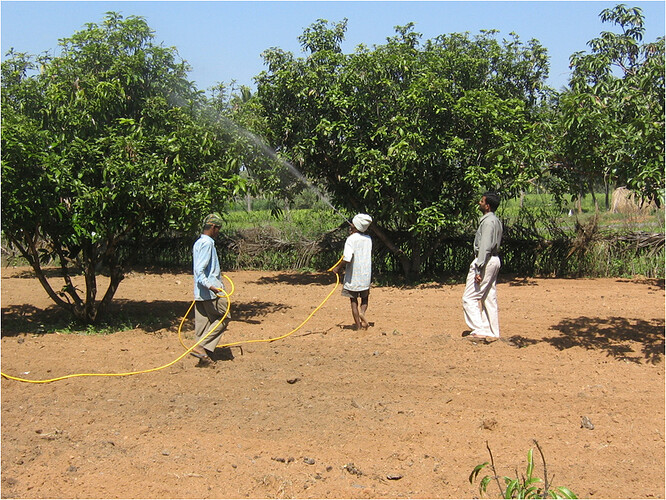
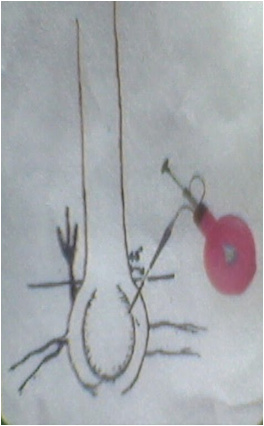
ROOT FEEDING
Application of nutrients in the form of liquid directly to root of the plant
Select pencil thickness feeding root –
white / light yellow / pink colour root – not black or dark brown


 Make a slanting cut at tip of the root
Make a slanting cut at tip of the root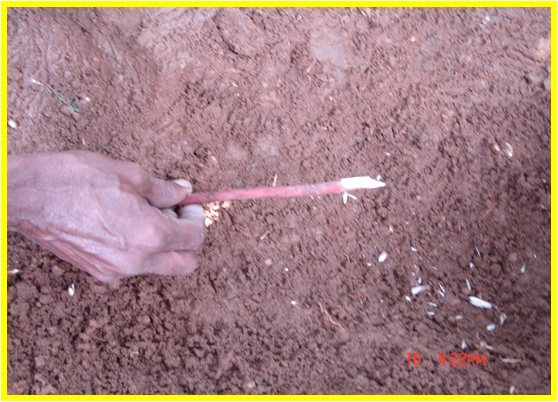
Cut the tonic pocket at one corner or
add 200 ml diluted tonic to opened polythene pocket


Insert the root into the tonic pocket and tightly
tie with twine


 Trunk Feeding
Trunk Feeding


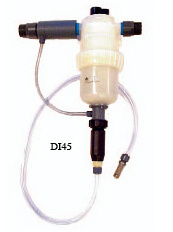
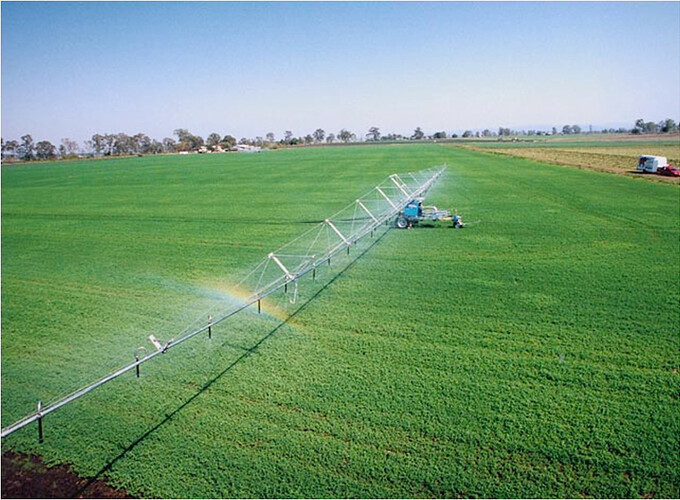
 Fertigation
FertigationApplication of nutrients / fertilizers especially water soluble fertilizers through irrigation water to the plants
 Methods used fertigation
Methods used fertigation Drip Irrigation
Drip Irrigation

Sprinkler Irrigation

FERTIGATION SYSTEM
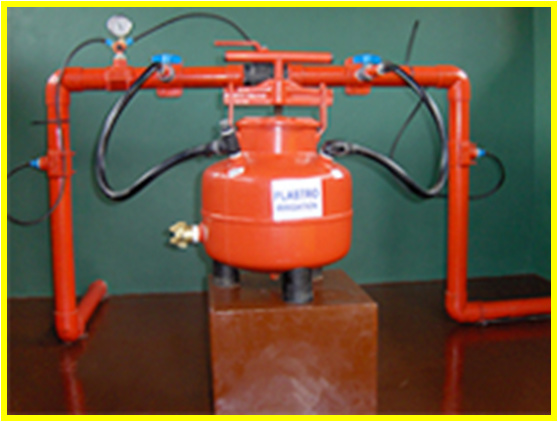

 Advantages of Fertigation
Advantages of Fertigation
 Application exactly at root zone
Application exactly at root zone
 Reduction in fertilizer quantity
Reduction in fertilizer quantity Reduced leaching loss
Reduced leaching lossApplication of nutrients at the correct time
No need of extra manpower for nutrient application